
Lookalike domains and how to spot them
Fake websites and email addresses are often used in phishing and targeted attacks. How do fake domains get created, and how to spot one?
28 articles

Fake websites and email addresses are often used in phishing and targeted attacks. How do fake domains get created, and how to spot one?

Cybercriminals can access the e-mails of folks you’re in correspondence with and then try to hijack your conversations.

Apple’s new feature promises enhanced protection in the fight against targeted attacks.


The most active groups targeting companies, encrypting data, and demanding ransom.

CD Projekt confirms attack on internal systems. Hackers claim to have downloaded Cyberpunk 2077 and The Witcher 3 source code, and demand ransom.

The Lazarus cybercrime group uses traditional APT techniques to spread VHD ransomware.

Our experts detected a malware framework that cybercriminals use to attack various operating systems.

Even if a computer is physically isolated, data can be stolen from it using some very unusual methods.

MITRE tested our solutions in the APT29 evaluation. We explain what the test is, why and how it’s conducted, and what the results mean.

The Brothers Grimm fairy tales are deep source of object lessons in information security — not just for children, but also for adults.

A Chrome vulnerability already exploited by attackers gets patched. We recommend updating your browser right now.

In this episode, Jeff sits down with Vicente Diaz of Kaspersky Lab’s GReAT to discuss a review of APTs in 2018 and what 2019 may hold.

Malefactors do not need to infect your computers with malware if they can just plug their devices right into your network.

More than 400 manufacturing companies became phishing targets.

The most common definition of security intelligence is knowing how your business may be attacked. This is an important part of security expertise, but it’s not the only one.

Kaspersky Lab’s security experts released a detailed report on Operation Ghoul – a targeted campaign aimed primarily at businesses in the Middle East and Europe.

Cyberweapons have to communicate to their creators, propagate within the infrastructure and send data. That’s when an effective and highly flexible algorithm can be capable of spotting them.
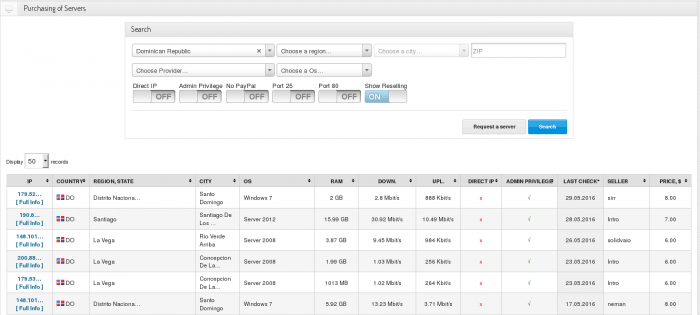
Kaspersky Lab has lately researched an active cybercriminal trading platform xDedic. The main purpose of the xDedic marketplace is to facilitate buying and selling credentials of more than 70,000 hacked servers from all around the world.

One of the most popular techniques used to penetrate corporate defenses is the use of vulnerabilities found in working software, which, in fact, do not need to be brand-new 0-days.

Instead of writing their own malicious tools, criminals are increasingly using the off-the-shelf malware, and more and more often – totally legitimate software.